In the modern healthcare ecosystem, speed, accuracy, and real-time decision-making are critical—especially during emergencies. With the increasing demand for intelligent healthcare solutions, IoT-based smart stretchers are emerging as a game-changing innovation in hospitals and emergency medical services. These stretchers not only assist in patient transportation but also integrate vital sign monitoring and GPS tracking, ensuring patient safety and enhancing clinical efficiency.
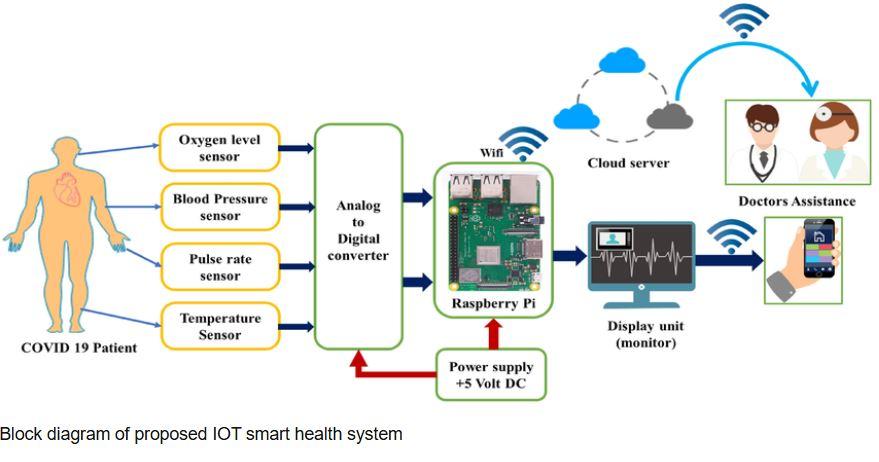
The block diagram above represents a proposed smart health monitoring system built using IoT technology. It illustrates how various sensors—such as oxygen level, blood pressure, pulse rate, and temperature sensors—are attached to the patient and continuously collect vital health data. These analog signals are passed through an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) to be interpreted by the Raspberry Pi, which serves as the system’s processing unit.
Once processed, the vital information is transmitted in real time via Wi-Fi to a cloud server, making the data accessible to doctors and healthcare staff remotely. Simultaneously, a display unit (monitor) near the stretcher presents real-time readings, helping medical personnel closely monitor the patient during movement across hospital departments or ambulances. Additionally, the integration of mobile access ensures that on-duty doctors can receive alerts and health data on their smartphones for quick intervention.
The system is powered by a +5V DC power supply, ensuring portable operation, and can also be expanded to include GPS modules to track stretcher location, which is crucial in large hospital environments or during outdoor patient transfers.
This report delves into the system’s architecture, component selection, data flow, communication modules, and the role of cloud integration in making smart stretchers more efficient, intelligent, and patient-centric.

.svg)