With the rapid advancement in embedded systems and wireless communication technologies, automation and remote control systems have become increasingly popular in engineering projects. One such widely implemented and educationally valuable project is the Bluetooth Controlled Car, which demonstrates the integration of wireless communication, microcontroller programming, and motor control in a compact system.
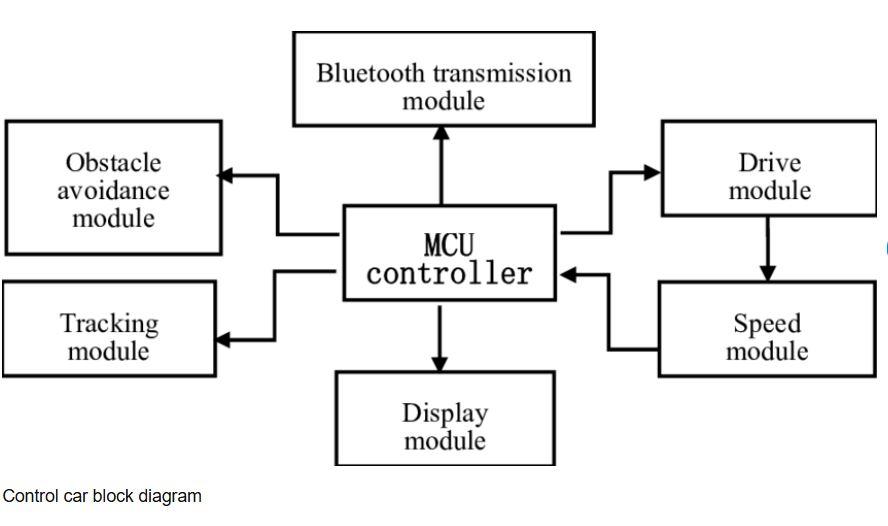
A Bluetooth-controlled car is a type of robotic vehicle that can be controlled wirelessly using a smartphone or any other Bluetooth-enabled device. It eliminates the need for physical remote controls or wired connections, enhancing mobility, flexibility, and user convenience. The system is built around a microcontroller (commonly Arduino Uno or NodeMCU) which acts as the brain of the vehicle. A Bluetooth module (like HC-05 or HC-06) receives commands from the user’s mobile application and sends them to the microcontroller. Based on the received signals, the microcontroller controls the movement of the car by driving the motors via a motor driver module (typically L298N).
The vehicle can be controlled in multiple directions such as forward, backward, left, and right, and it can also be stopped with the press of a button on the smartphone. The main advantage of this system is its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to demonstrate core concepts of robotics, wireless communication, and embedded systems, making it an ideal choice for beginners and college-level engineering students.
This report explains the components used, working principle, circuit diagram, programming logic, and the real-world applications of the Bluetooth-controlled car. It also highlights future enhancements such as obstacle detection, voice control, and integration with IoT for smart automation.

.svg)